UAV - Unmanned Aircrafts
Also when flying an unmanned aircraft/drone you need to talk to Air Traffic Control and other aircrafts.
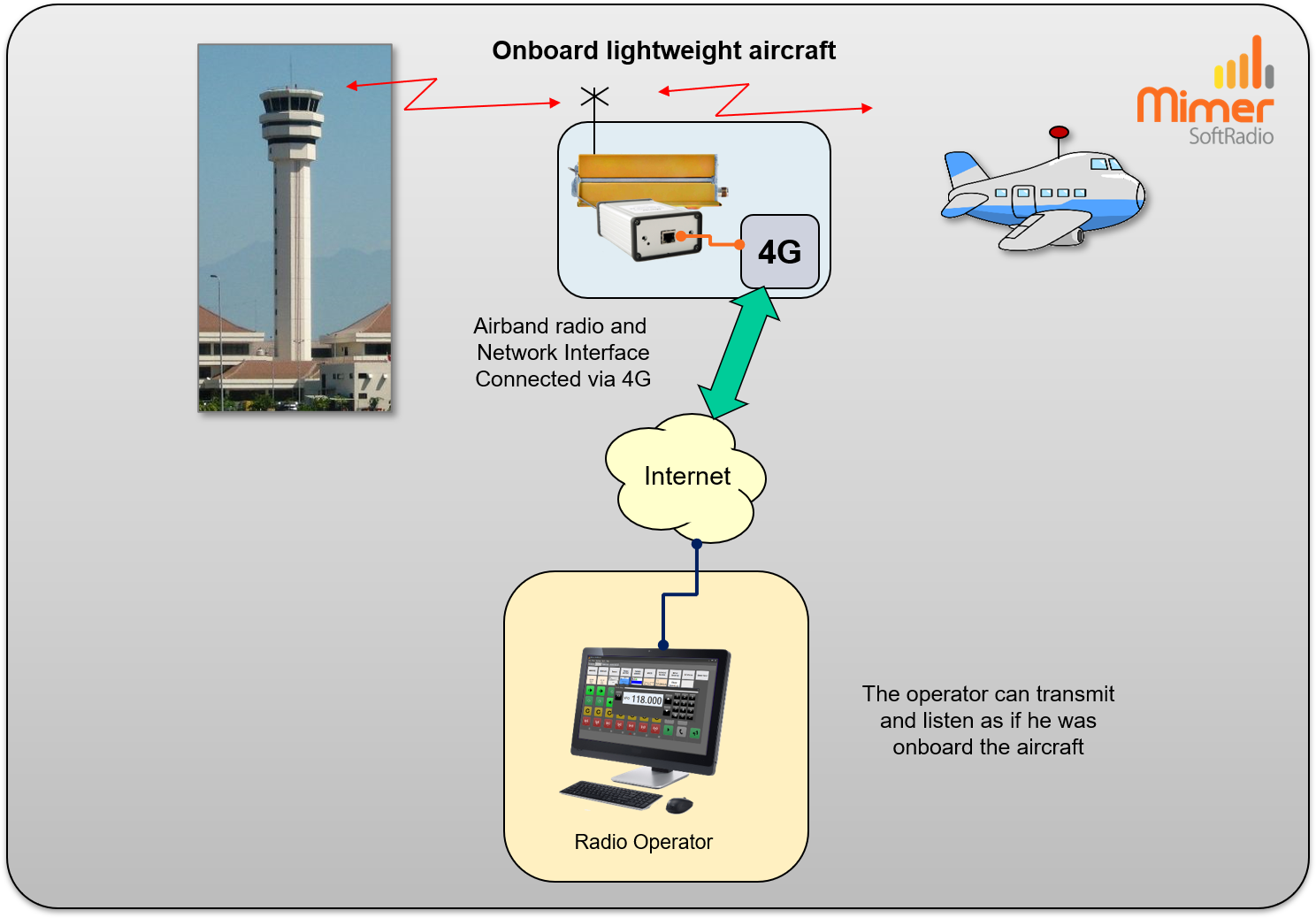
Using SoftRadio, you can place the airband radio close to where you are flying or even onboard the aircraft. While the pilot / radio operator is somewhere else.

Different ways of placing the radio
When flying your UAV within radio coverage of the “Tower”, you can most likely use a portable radio to alert the closest Air Traffic Control.
But when flying further away or even between the coverage of two different “Towers”, you might need to boost your own coverage.
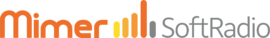
Radio in a high position close to the flight
With the radio and the antenna in a high position, you will get much better coverage. You can then remote control the radio using an IP connection. Either if you have access to an Internet land line or you can use a 4G/5G modem.
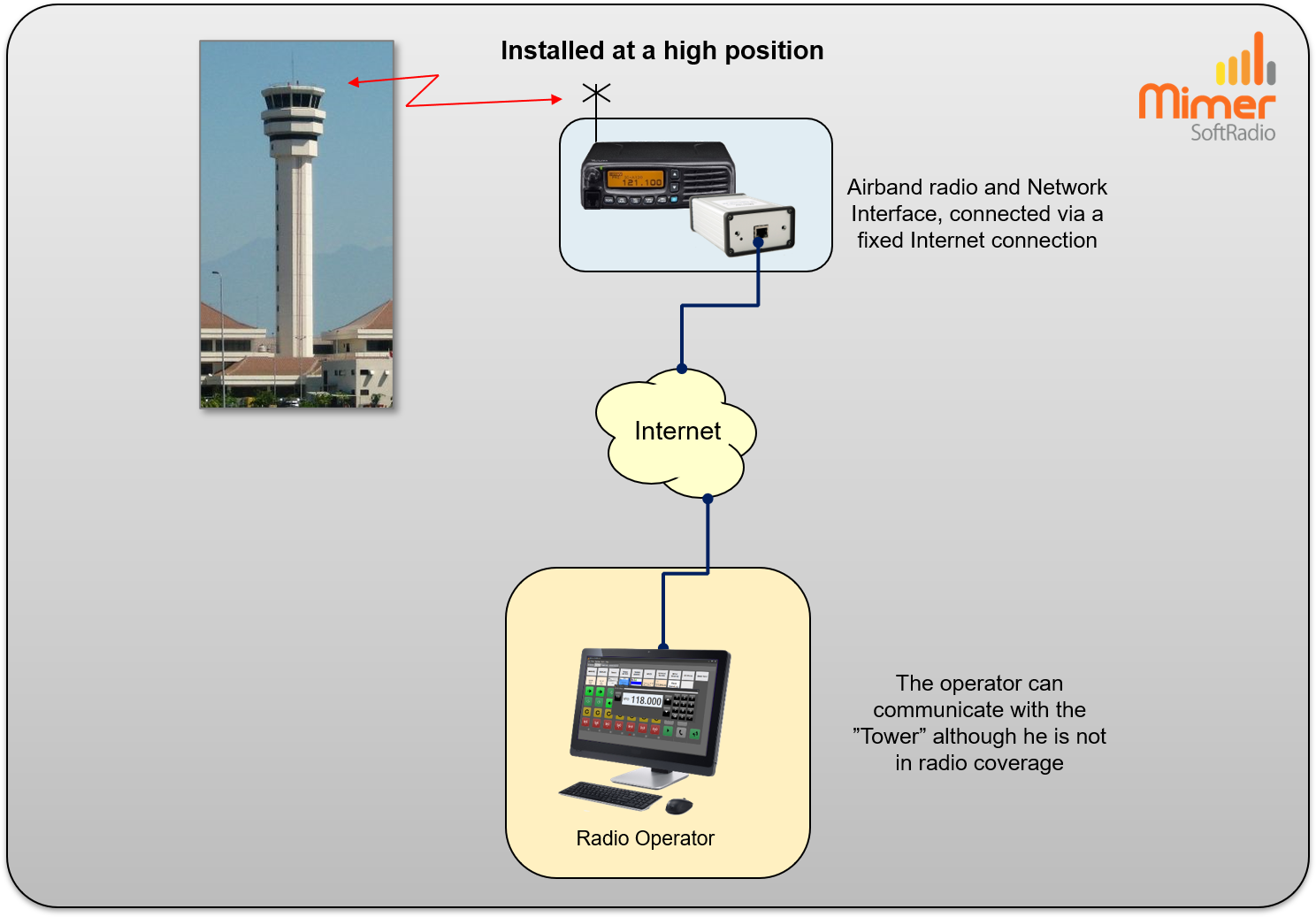
Radio onboard the drone
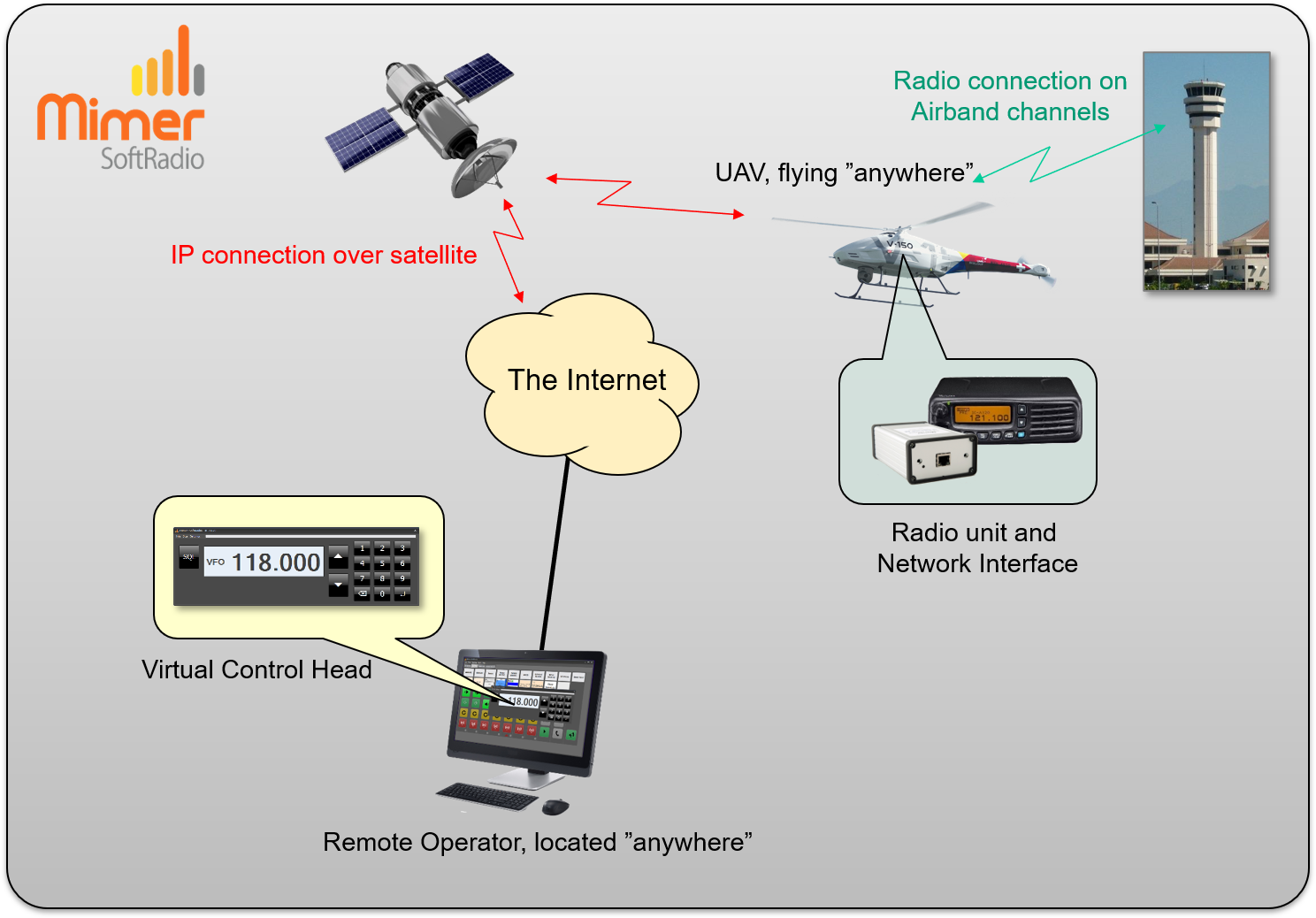
With the radio onboard the UAV your radio will work in the same way as if you yourself where onboard and talking to the “Tower”.
To remote control the onboard radio you need to use IP over 4G/5G when available or satellite when cellular is not available. These are similar setups to those we make for unmanned ships at sea.
To keep the onboard equipment as light as possible, we recommend the Trig TY91 radio.
We get more and more requests for light weight solutions. Systems that might be onboard an unmanned aircraft (drone).
Here is a setup with a Trig TY91 and setups with a Yeasu portable and with an Icom portable airband radio.
Examples of using SoftRadio with UAV´s
Flying between hospitals in a city
Both in Belgium and in Norway, SoftRadio has been involved in tests with UAV´s that fly between hospitals. They carry tests, blood etc. much faster than a city transport with car can be made.
In order to clear that the air is free for flying, the drone pilot needs to talk to the tower at the nearest airport. When they do so, using a radio, all other aircraft that are close by also gets the same message.
In the first tests the airband radio have been left on the ground connected over the Internet to the pilot, so that he can be “anywhere”. In a later stage the radio might instead be onboard the drone, in the same way as unmanned ships have radios onboard.
Flying between mainland and islands or oilrigs
When flying a longer distance you will most likely need to use your airband radio to talk to the air traffic control at both ends of the flight. The only practical way to do this is to install the the airband radio onboard the UAV and remote control it from the pilot position. The communication with the “towers” will be just as if you were onboard the aircraft.
We have done several setups for this purpose and also sell the very small airband radio from Trig that can easily be installed onbord.
Flying for surveilance or maintenance
When flying not only a long distance but also for many hours, maybe for doing maintenance along power lines or surveilance in marine and military environments, you will also need to have the radio unit in the UAV.
There is a big chance that you will “meet” another flying object and you then need to quickly identify yourself over the airband radio.
We have done several setups for this purpose and also sell the very small airband radio from Trig that can easily be installed onbord.
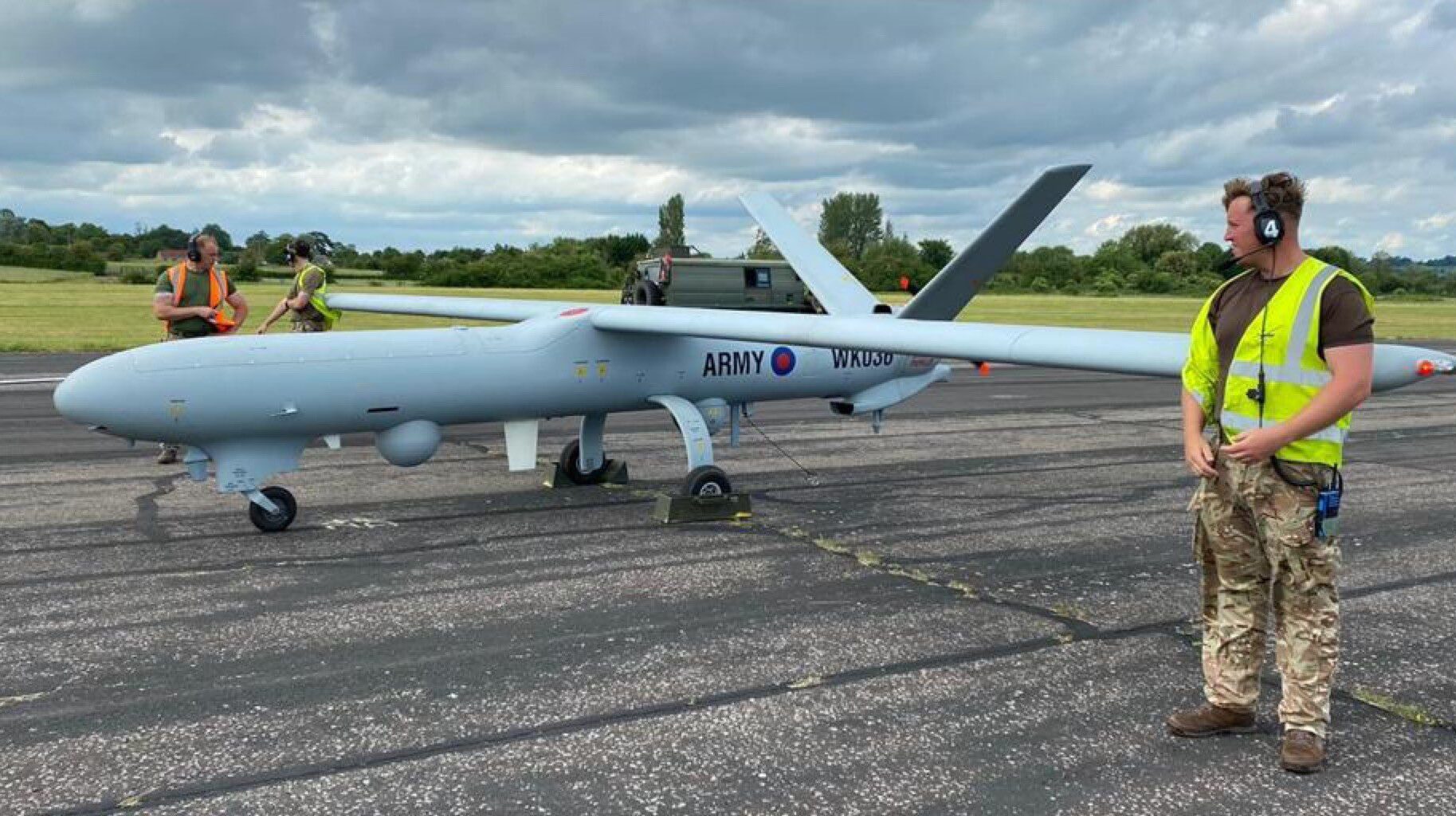
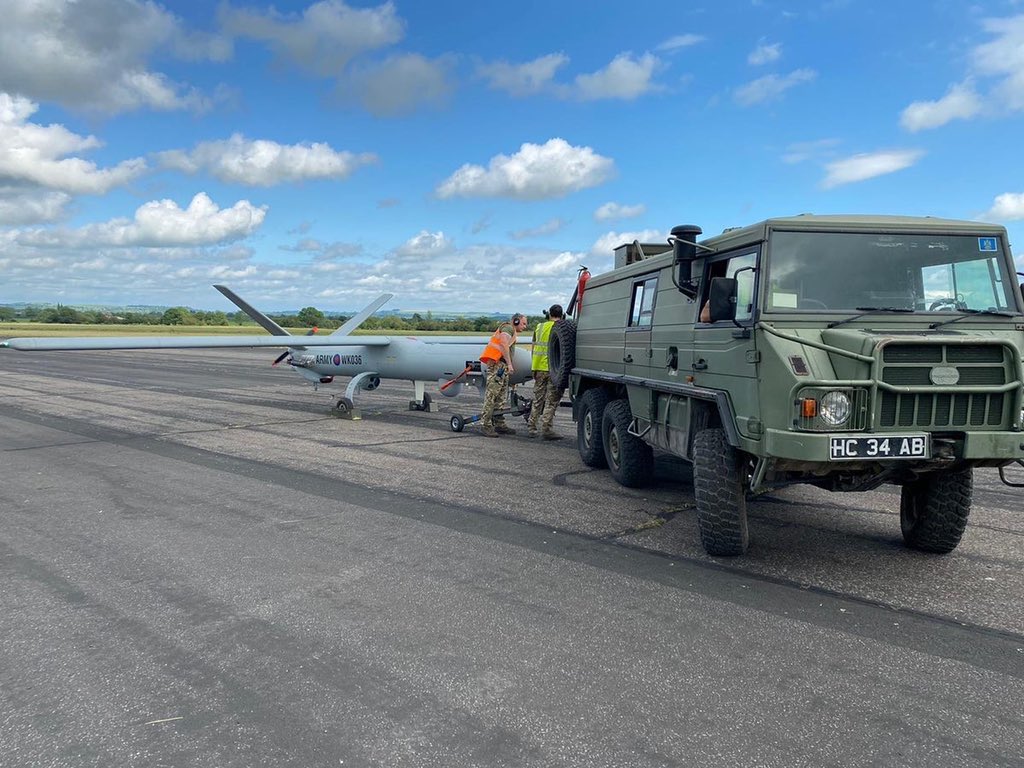
Customer case with the UK Armed Forces
47th Regiment Royal Artillery operates the Watchkeeper Remote Piloted Air System (RPAS), providing the British Army with Tactical Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance (ISTAR). The Watchkeeper RPAS is able to fly for 14 Hours and carries an Electro Optical / Infra Red and Radar Payload. The system is normally flown from MOD Boscombe Down with fully functional Air Traffic Control (ATC) and airfield facilities.
As part of a 90 Day Exercise designed to challenge, develop and test their Tactics, Training and Procedures, the Regiment has deployed to Keevil Airfield in Wiltshire which has no ATC or airfield facilities. Keevil Airfield is based in a valley north of Salisbury Plain Training Area (SPTA) and due to its lower elevation, there is no line of sight with Boscombe Down ATC 30 km away. From Keevil Airfield, the Watchkeeper RPAS is flown into SPTA where it supports British Army training on sorties lasting 6 – 8 hours, whilst remaining in constant communications with Boscombe Down ATC.
In order to improve safety by adding another method of communicating with Boscombe Down ATC, 47th Regiment Royal Artillery has employed the MIMER SoftLine system from Brabourne to create a Radio over Internet Protocol (RoIP) repeater to bridge the high ground in between Keevil and Boscombe Down.
The system is connected to an ICOM IC-120E on either end, with the link between the 2 radios being connected through the SoftLine and internet. This allows the Watchkeeper Pilots to operate using their internal radios to communicate with Boscombe ATC without direct line of sight which adds yet another layer of safety to their Operations from Keevil Airfield.
The versatility and ease of operation of the Mimer System will allow 47th Regiment to employ this equipment on future deployments, when operating in remote areas of the world supporting our Troops.
Set up in cooperation with Brabourne Communications in the UK.
Helpful SoftRadio Options
- Satellite mode
There are special versions of our servers to handle the latency and jitter over a satellite link.
Read more here.
- Low Bandwidth
We have an option to the Network Interface that reduces the bandwidth needed. Practical when every byte costs, for example over satellite.
Read more here.